
Under the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China projects
(approval numbers: 82025002, 82394411, 82170113), the team of Professor Zhang
Huiyuan and Researcher Hu Hongbo from the Institute of Immunology and
Hematology/National Key Laboratory of West China Hospital of Sichuan University,
in collaboration with Professor Liu Xindong from Southwest Hospital of Army
Medical University, has made progress in the research of allergic asthma. The
research findings, titled "Hypoxia inducible factor 2 α promotes pathogenic
polarization of stem like Th2 cells via modulation of phospholipid metabolism by
regulating phospholipid metabolism," were published on December 10, 2024 in the
journal Immunity. Paper link: https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/ S1074-7613
(24) 00496-5.
Allergic asthma (abbreviated as asthma) is a common chronic respiratory
immune disease, and its pathogenesis is mainly related to the abnormal
activation of T helper 2 cells (Th2 cells) induced by allergens. Traditional
treatment methods such as bronchodilators and glucocorticoids can effectively
alleviate the symptoms of asthma patients, but cannot achieve a complete cure
for asthma. In addition, for patients with severe asthma, drug resistance
further limits the efficacy of existing treatment options. Therefore, exploring
new treatment strategies, especially precise targeted therapy for pathogenic Th2
cells, has become a key research direction in the field of asthma treatment.
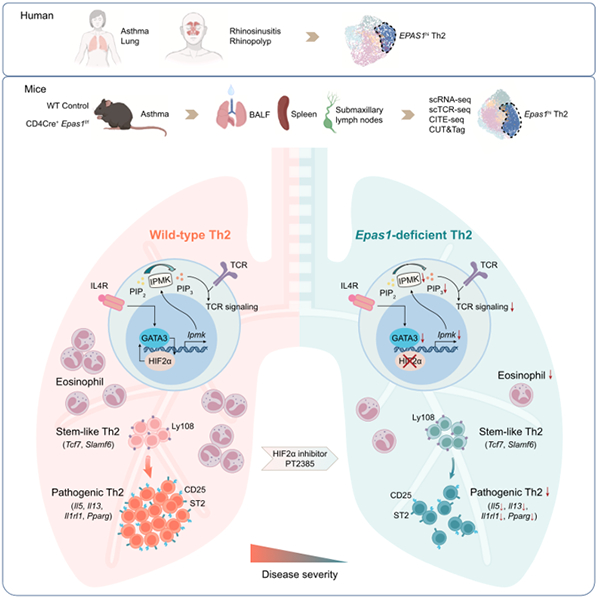
This study conducted single-cell analysis of CD4+T cells in patients with
asthma and chronic sinusitis, and found that the expression of HIF2 α was
significantly increased in pathogenic Th2 cells. Further experimental results
showed that T cell specific knockout of HIF2 α significantly inhibited the
differentiation of Th2 cells and alleviated asthma symptoms in mice. This study
describes the heterogeneity of Th2 cells in asthma and reveals the core
regulatory role of HIF2 α in the transformation of dry like Th2 cells into
pathogenic Th2 cells (Figure). Based on the above findings, the study further
evaluated the therapeutic potential of the HIF2 α - specific inhibitor PT-2385.
The results showed that PT-2385 can significantly inhibit Th2 cell
differentiation, effectively alleviate airway inflammation, and control asthma
symptoms.
This study elucidates the key role of HIF2a in promoting phospholipid
metabolism and regulating Th2 cell differentiation in the pathogenesis of
allergic asthma, providing a new perspective for a deeper understanding of the
immune pathogenesis of asthma and offering new ideas for precise targeting of
HIF2 α in the treatment of allergic asthma.